The programme
Here you can find an overview of the degree programme, including information on its organisation and regulations, as well as a number of useful information. In addition, this section includes an overview of the University’s Quality Assurance system and the Student Orientation services available to prospective students, to help them choose the right course for them.
Student orientation services
The new website of the Student Orientation Office, with new form and content, is the result of a long process aimed at providing a better and more comprehensive service to its many users. Users are mostly secondary school pupils approaching the University for the first time, and schools' University Orientation Services which organise activities to assist their pupils in post-school choices. Making a decision means choosing the best alternative to satisfy one's expectations, preferences and aspirations.
More details: www.univr.it/orientamento (italian page)
Email servizio.orientamento@ateneo.univr.it
Telephone number 0458028000
Timetable
Sportello telefonico: dal lunedì al venerdì, dalle ore 9:00 alle 13:00.
Find out more● Matematico-modellistico: enfasi su metodi e strumenti di tipo analitico/quantitativo e modellistico, con particolare riferimento alla teoria della Probabilità, all'analisi statistico-inferenziale, statistical learning, tecniche di ottimizzazione e selezione dei dati, anche con specifico riferimento a schemi numerici, e metodi e modelli della fisica dei sistemi complessi
● Informatico: enfasi su metodi e strumenti atti a sviluppare tecniche di data cleaning / data analysis /data visualization ed exploratory analysis, uso e sviluppo di software specifici in ambito machine learning, e deployment
● Management: sviluppo di conoscenza nell'ambito della cultura gestionale ed organizzativa d'impresa, anche in relazione all'organizzazione dei processi, delle decisioni per mezzo di strumenti nell'ambito dell'ottimizzazione dei processi aziendali e della business intelligence con particolare riferimento alla logistica, al marketing, ai problemi di customer segmentation/scoring/clustering, nonché in riferimento all'acquisizione di metodologie per la gestione e condivisione dei processi aziendali
● Giuridico: obiettivi specifici in questo settore sono quelli della conoscenza dei principi e delle fonti del Diritto privato e Diritto pubblico, delle normative (in ambito, e.g., privacy/NDA) sulla gestione dei dati
● Filosofico-Sociale: focus sull'acquisizione delle basi etico-filosofiche del valore del dato cosicché lo studente sappia trattare il dato stesso in senso etico anche in relazione al contesto produttivo nel quale sarà professionalmente inserito anche in relazione all'interpretazione dei fenomeni socio-economici connessi
PROFILI PROFESSIONALI
Funzione in un contesto di lavoro
Il data analyst ricopre ruoli di responsabilità nell'analisi di grandi moli di dati nell'ambito di un'azienda o di un'organizzazione, con l'obiettivo di estrarre e inferire nuova conoscenza utile alla comprensione della realtà e strumentale ai processi strategico-decisionali. Tipicamente questo ruolo richiede di combinare ed esplorare molteplici sorgenti di dati, sovente di grandi dimensioni (gestione big data) e non strutturati.
Competenze associate alla funzione
- Il data analyst, avendo acquisito competenze nell'ambito dell'analisi dati tanto dal punto di vista matematico/statistico che informatico, saprà rispondere efficacemente a problematiche inerenti la preparazione dei dati, come, ad esempio, estrazione e pulizia di serie storiche, al fine di ottimizzarne e renderne più efficace l'analisi
- Il data analyst ha conoscenza di metodi statistico inferenziali e relativamente alle tecniche di data mining e machine learning necessarie tanto in fase di analisi/aggregazione/organizzazione dei dati, quanto in relazione all'estrazione di nuova conoscenza da essi
- l data analyst ha acquisito padronanza degli strumenti e dei linguaggi di programmazione comunemente usati nel campo dell'analisi dei dati al fine di condurre analisi efficaci ed efficienti.
- Il data analyst ha appreso come operare efficacemente all'interno di team interdisciplinari: la data science sta all'intersezione tra informatica, matematica e applicazioni; per questo il data analyst, al termine del percorso di Laurea Magistrale in Data Science, è in grado di acquisire conoscenza di dominio e di interagire con esperti del settore.
Sbocchi occupazionali
I data analyst sono ricercati in tutti quei contesti aziendali e organizzativi, non necessariamente informatici, in cui è cruciale analizzare e interpretare grandi e/o complesse moli di dati. In quest' ambito ricadono anche istituti scientifici, laboratori e università.
Funzione in un contesto di lavoro
Il laureato svolge compiti legati all'applicazione ed allo sviluppo di modelli probabilistico/analitici per estrarre proprietà di dati ed effettuarne il relativo studio e progettazione in ambito predittivo, nonché compiti legati allo sviluppo di nuovi algoritmi statistico/probabilistici per ottimizzare i processi aziendali.
Competenze associate alla funzione:
• Il data scientist possiede competenze avanzate di utilizzo e sviluppo di algoritmi basati sulla teoria della Probabilità, dei processi stocastici, ciò che gli consente di interagire efficacemente all'interno di gruppi di lavoro orientati all'analisi dei dati e dell'estrazione di valore da essi, al fine di sviluppare modelli di categorizzazione e forecast;
• Le competenze in ambito machine learning permettono al data scientist di produrre soluzioni concrete per l'implementazione di algoritmi predittivi anche in relazione all'uso dei software di analisi dati e matematico/statistici tipicamente usati nel mondo industriale ad alto contenuto di innovazione
• Il data scientist ha appreso le principali tecniche di ottimizzazione algoritmica, conoscenze che gli permettono di agire efficacemente sulla (ri)strutturazione di complesse soluzioni software eventualmente già in essere nel contesto lavorativo di impiego
• Il data scientist ha acquisito conoscenze informatico/matematiche che gli permettono di interagire con colleghi programmatori, esperti in sviluppo front-end/back-end, anche in relazione alla gestione di data base e recupero informazioni via API.
• Il data scientist avrà appreso competenze anche nell'ambito business intelligence, ed economico così da poter integrare velocemente ed in modo fattivo le proprie capacità matematico/informatiche al fine di rispondere in modo efficace e completo alle problematiche caratterizzanti i processi di creazione di modelli analitico/predittivi caratterizzanti processi industriali eterogenei come, ad esempio, problemi di categorizzazione e previsione a valere su serie storiche multivariate.
Sbocchi occupazionali
I data scientist sono ricercati tanto in ambito industriale manifatturiero (ad esempio pro efficientamento processi di produzione), quanto in ambito finanziario (ad esempio per lo sviluppo di modelli previsionali) e pubblico (ad esempio per la razionalizzazione dei processi di lavoro). Sovente i data scientist trovano impiego nei centri di ricerca e sviluppo, tanto privati (aziende farmaceutiche, provider di servizi/soluzioni in ambito informatico), quanto afferenti ad istituzioni pubbliche (università e centri di eccellenza).
Governing bodies
Quality Assurance
The quality of a degree programme is the extent to which it achieves its educational objectives and meets the quality requirements of the educational activities offered, which are determined in line with the needs and expectations of students and representatives of the world of work.
- periodic consultations with representatives of the world of work to assess the adequacy of the cultural and professional profiles offered in their courses;
- design of educational contents and planning of resources;
- organisation of educational activities and teaching services;
- monitoring the effectiveness of teaching and planning measures to improve teaching and services;
- provision of complete and up-to-date information on its website, relating to the programme (professional roles, expected learning outcomes, learning activities).
In a Quality Assurance system, students play a fundamental role: each student can play their part by participating in the Quality Assurance groups of their degree programme and in the Faculty-Student Joint Committees or, more simply, by taking part in the Student Survey on teaching, or questionnaires. It’s in this context that specific workshops for student representatives (‘Laboratori di rappresentanza attiva’) are periodically made available to students by the University and the University’s Quality Assurance Board. To find out more, please see the relevant section.
Il sistema di valutazione universitario e il ruolo dello studente
by Prof. Graziano Pravadelli: a lecture recorded on the occasion of the January 2021 workshop for student representatives.
QA bodies
QA in degree programmes
QA activities
Degree Programme description and regulations
Not yet available
The Degree programme teaching regulations, published on june/july set out the organisational aspects of the degree programme, in line with the University’s teaching regulations. It includes general information about the programme, links to the relevant module web pages and specifies the administrative aspects.
Other Rules
The Italian University system
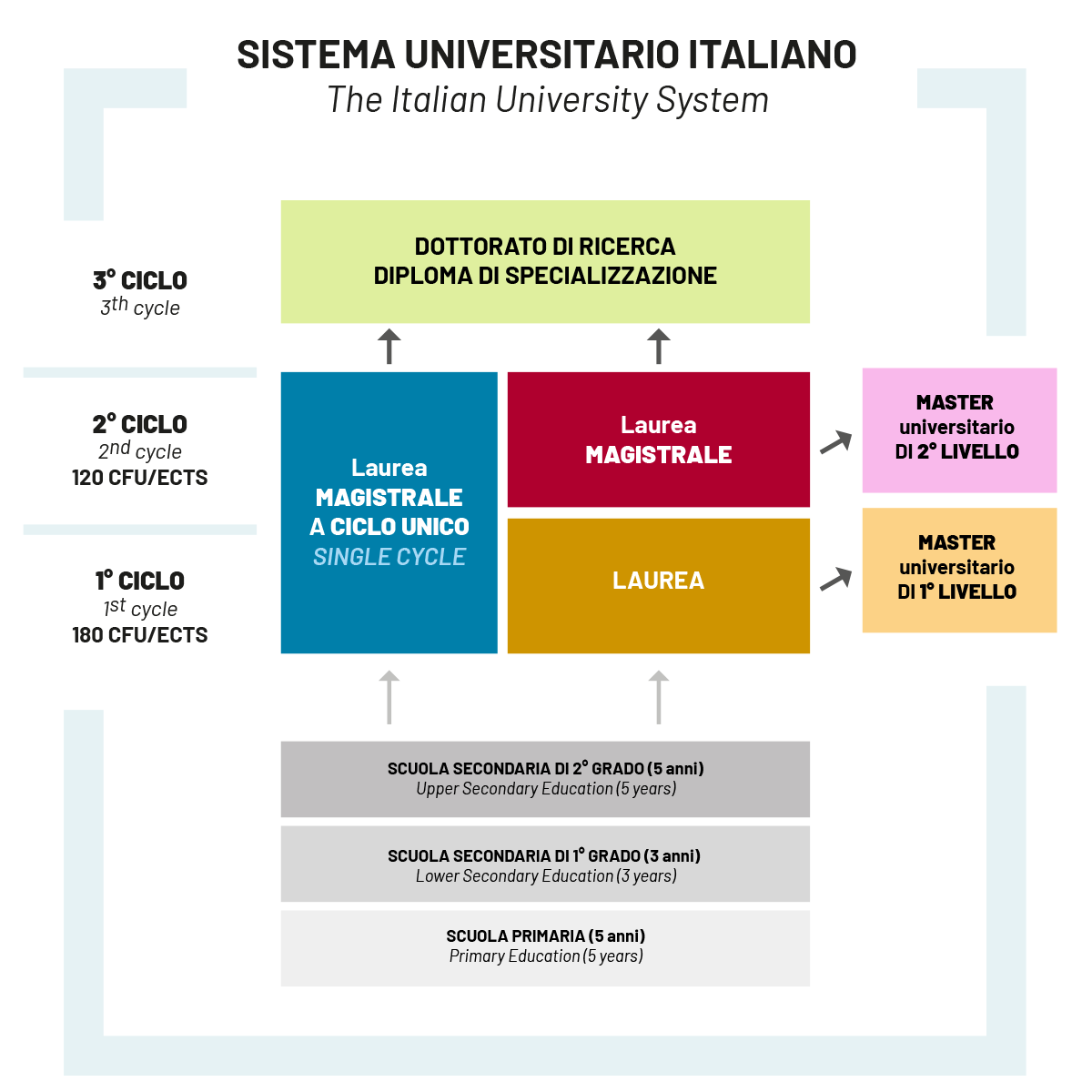
First-cycle degrees: Bachelor’s degree programme
First-cycle degrees are aimed at enabling students to achieve a command of general scientific methods and content, and to acquire specific professional knowledge.Admission requirements: secondary school diploma after completing 13 years of study in total and passing the relevant State examination, or equivalent foreign qualification; admission may be subject to further assessment.
Duration: three years.
Graduation: in order to obtain the degree, it is necessary to gain at least 180 CFU; doing an internship and preparing a dissertation/thesis may also be required. Upon completion of a Bachelor’s degree, graduates may continue their studies by enrolling in a Master’s degree or other second-cycle degree programmes and courses.
Academic title: upon completion of a Bachelor’s degree (Laurea), graduates are awarded the title of “Dottore”.
Second-cycle degrees: Master’s degree
Second-cycle degrees aim to provide students with an advanced training and knowledge to take on highly-skilled roles.Admission requirements: applicants must hold a Bachelor’s degree, or a foreign equivalent qualification; curricular admission requirements for each course may vary depending on each University.
Duration: two years.
Graduation: in order to obtain the degree, it is necessary to gain at least 120 CFU, as well as preparing and presenting a dissertation/thesis.
Academic title: upon completion of a Master’s degree (Laurea Magistrale), graduates are awarded the title of “Dottore magistrale”. Single cycle/Combined Bachelor+Master’s degrees
Some courses (Medicine and Surgery, Veterinary Medicine, Dentistry and Dental Prosthetics, Pharmacy and Industrial Pharmacy, Architecture and Building Engineering-Architecture, Law, Primary Education) are offered as Single cycle/Combined Bachelor+Master’s degrees (Corsi di Laurea Magistrale a Ciclo Unico).
Admission requirements: applicants must hold a secondary school diploma or equivalent foreign qualification; admission is subject to passing an admission test.
Duration: five years (six years and 360 CFU for Medicine and Surgery, and Dentistry and Dental Prosthetics).
Graduation: in order to obtain the degree, it is necessary to gain at least 300 CFU, as well as preparing and presenting a dissertation/thesis. Upon completion of a Single-cycle degree, graduates may continue their studies by applying for a PhD programme (Dottorato di Ricerca) or other third-cycle courses.
Academic title: upon completion of a Master’s degree (Laurea Magistrale), graduates are awarded the title of “Dottore magistrale”.
Third-cycle degrees
PhD programmes: these courses enable students to gain reliable methodologies for advanced scientific research through innovative methodologies and new technologies, and generally include internships abroad and lab activities at research laboratories. Graduates wishing to apply for a PhD programme must have a Master’s degree (or a foreign equivalent qualification) and pass an open competition; PhD programmes have a minimum duration of three years. In order to complete the programme, students must produce a research thesis/dissertation and present it at a final examination.Academic title: upon completion of a PhD programme, students are awarded the title of “Dottore di ricerca”, or “PhD”.
Postgraduate specialisation courses: these are third-cycle courses aimed at enabling students to develop advanced knowledge and highly-specialised skills, such as in the medical, clinical and surgical fields. To be admitted to these courses, applicants must have a Master’s degree (or a foreign equivalent qualification) and pass an open competition. Postgraduate specialisation courses may last from two (120 CFU) to 6 years (360 CFU) depending on the type. Academic title: upon completion of this programme, graduates are awarded a “Diploma di Specializzazione”.
Professional Master’s programme
1st-level Professional Master’s programmes: these courses enable students to further enhance their scientific knowledge and professional skills. In order to apply, applicants must have a Bachelor’s degree, or foreign equivalent qualification. The minimum duration is one year (60 CFU). Please note that completing this course will not provide you with direct access to a PhD programme (Dottorato di Ricerca), or other third-cycle courses, as these courses are run and managed by each University at the local level. Upon completion of this programme, students are awarded a “Master universitario di primo livello”.2nd-level Professional Master’s programmes: these courses enable students to further enhance their scientific knowledge and professional skills. In order to apply, applicants must have a Master’s degree, or foreign equivalent qualification. The minimum duration is one year (60 CFU). Please note that completing this course will not provide you with direct access to a PhD programme (Dottorato di Ricerca), or other third-cycle courses, as these courses are run and managed by each University at the local level. Upon completion of this programme, students are awarded a “Master universitario di secondo livello”.
Other useful things
Crediti Formativi Universitari (CFU/ECTS credits): Italian university courses are based on the CFU system. 1 CFU is equal to 25 hours of study. The average annual academic workload for a full-time student is generally assumed to be 60 CFU. CFU and ECTS credits serve the same purpose and generally have the same value.Degree class: Bachelor's and Master's degree programmes that have the same learning objectives and activities are grouped into “degree classes". The educational content of each programme is set autonomously by each university; however, universities are required to include certain educational activities (and the corresponding number of CFU credits) set at the national level. These requirements are established in relation to each degree class. Degrees in the same class have the same legal value.
Double/Joint degrees: the Italian universities may establish degree programmes in partnership with other Italian or foreign universities. Upon completion of these courses, graduates are awarded a joint or double/multiple degree, one from each Partner University.
